The Whole Brain® Thinking Methodology
The most advanced system ever developed to measure and define cognitive diversity.


The Whole Brain® Thinking Methodology
The Whole Brain® Thinking methodology is a powerful, science-backed operating system for decoding and harnessing the cognitive diversity of individuals, teams, and organizations. This methodology is the basis of the HBDI® assessment and the tools that leverage the language and insight for scalable applications of all learning.
We all have access to our Whole Brain® and are constantly activating many different areas simultaneously. During our lives, our brains naturally develop patterns as we learn and engage with the world. Our thinking patterns ultimately emerge as preferences — and the Whole Brain® Model decodes what that means for you and your team.
The Whole Brain® Model is a metaphor for how we think. But it’s also a practical approach to observing and describing our thinking preferences — and the preferences of those around us. Equipped with this knowledge and language, you, your team, and your organization can unlock better thinking, performance, and results.
The Whole Brain® Model benefits workplaces at three levels:
- You understand your thinking preferences and how to apply that knowledge to improve your problem-solving, decision-making, communication, productivity, and well-being.
- Teams build a common language to frame their approach to cognitive diversity, which improves communication, team effectiveness, engagement, trust, and psychological safety.
- Organizations leverage thinking preferences via the common language and tools to increase organizational effectiveness, develop and retain top talent, increase revenue, and spur collaboration and innovation.
-14597.png)
What Is Whole Brain® Thinking?
Each of us has preferred methods and modes for navigating the world — from which hand is dominant to how we make sense of the world around us. Our thinking preferences affect where our attention and energy is directed and how we process information.
The Whole Brain® Thinking model provides a road map for understanding your thinking preferences and other people’s. That self-awareness allows you to move beyond your preferred thinking when the situation requires — giving you specific tools and stretching you into the practice of Whole Brain® Thinking.
Everyone has access to every thinking preference, even those they don’t prefer or gravitate toward. The Whole Brain® model helps us understand what we prefer and prioritize in our thinking, which informs our behavior. But to fully comprehend how this framework can benefit you, your team, and your organization, it is necessary to have a deeper understanding of the components that make up the model.
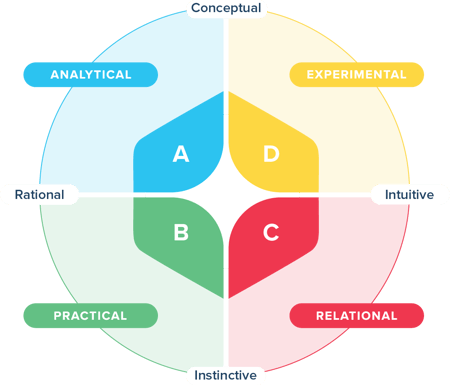
The 4 Quadrants of the Whole Brain® Model
The Whole Brain® Thinking model is based on four thinking preferences and each is assigned a quadrant. Each quadrant is different but equally important — no one thinking preference is “right” or better than another.
The best part? Everyone has aptitude and potential in each thinking preference quadrant, and no quadrant is considered better than any other. You simply require the tools and resources to unlock all four quadrants in your thinking.
-
Upper Left Blue A Quadrant: Analytical
-
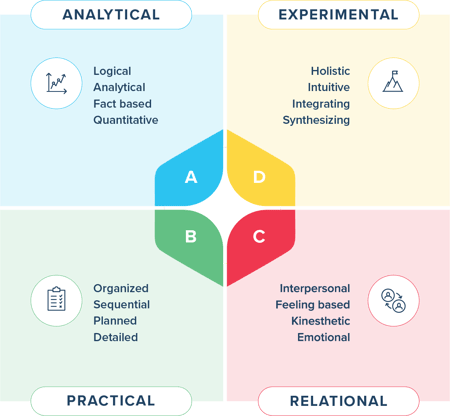
Thinks things through logically and methodically; good at problem-solving and making decisions.
-
Color significance: Blue — clear and to the point.
-
The upper left A quadrant typifies logical processing. The color chosen to represent this quadrant is cerulean blue — clear and to the point.
-
-
Lower Left Green B Quadrant: Practical
-
Applies knowledge to real-world situations; adept at organizing, planning, taking action, and managing.
-
Color significance: Green — grounded and pragmatic.
-
The lower left B quadrant typifies structured and organized thinking. The color chosen to represent this quadrant is green, suggesting groundedness.
-
-
Lower Right Red C Quadrant: Relational
-
Very expressive, Interacts well with others, and fosters relationships; effective at communicating and collaborating.
-
Color significance: Red — emotional and warm.
-
The lower right C quadrant typifies emotional, feeling, and interpersonal orientations. The color chosen to represent this quadrant is red because of the emotional passion implied.
-
-
Upper Right Yellow D Quadrant: Innovative
-
Thinks creatively and is open to trying new things; loves concepts, generates new ideas, and envisions the big picture.
-
Color significance: Yellow — vibrancy and energy.
-
The upper right D quadrant typifies imaginative qualities. The color chosen to represent this quadrant is yellow because of that color’s vibrancy.
-
We use all four quadrants of our Whole Brain® in our daily lives, although most of us feel more comfortable with certain thinking than others. Measuring the degree of those preferences is the foundation of the Herrmann Brain Dominance Instrument® (HBDI®).
Left Brain/Right Brain vs. Whole Brain® Thinking
Whole Brain® Thinking isn't the same as the left brain/right brain model you might be familiar with.
The concept of the left brain/right brain is inaccurate in depicting how the brain works. The left and right hemispheres are interconnected — in other words, we're “hardwired” to be whole-brained.
The Whole Brain® Model doesn't categorize people as right- or left-brained thinkers. Instead, it plots thinking preferences on four scales — analytical, practical, relational, and experimental. These scales are derived from combinations along two underlying axes: rational versus intuitive thinking and intellectual versus instinctive thinking.
What Is the HBDI®?
The HBDI® assessment is a popular tool for understanding individual thinking preferences, used by over 4 million people in more than 60 countries worldwide. It is considered one of the most comprehensive and practical assessments available. Fortune 100 organizations have utilized the HBDI® assessment, which has also been translated into more than 25 different languages.
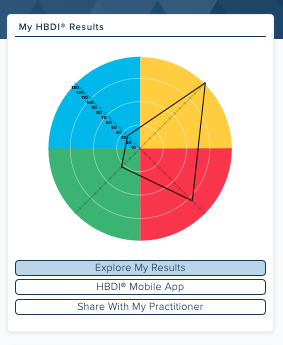
The HBDI® is a thinking-preferences assessment based on the Whole Brain® Thinking model that reveals your natural problem-solving, communication, and decision-making preferences. The HBDI® measures an individual’s degree of preference across the four quadrants of Whole Brain® Thinking and uncovers clusters of preferences.
Your HBDI® profile provides an accessible way to understand your thinking preferences and decode your preferred thinking clusters. With this knowledge, you can examine how those preferences affect your choices and effectiveness — and how they differ from those of the people you live, work, and interact with.

How Were Whole Brain® Thinking and the HBDI® Developed?
Whole Brain® Thinking was developed in the workplace, for the workplace. During his time as management education leader at General Electric, Ned Herrmann became interested in the effects of thinking styles and preferences on management and leadership development. Based on extensive research, Herrmann concluded that the brain can be divided (metaphorically) into four quadrants. Each is associated with different thinking, decision-making, and problem-solving preferences.
Based on his Whole Brain® Thinking model, Herrmann developed a series of questions to identify a person's dominant thinking style and degrees of preference across quadrants. These questions became the basis for the HBDI®.
At Herrmann, we’ve always believed that cognitive diversity has a significant impact on how people manage and lead — and our research has borne out that truth time and time again. Today, more than four decades of research and innovation stand behind the validity of the Whole Brain® Thinking model and the HBDI®.
What started as a traditional pencil-and-paper assessment has become a comprehensive talent intelligence platform. Herrmann’s platform provides lasting value through cutting-edge insights into your team’s thinking preferences and guidance for making the most of cognitive differences.
When everyone on your team actively applies Whole Brain® Thinking, you create a community of self-aware, self-reflective thinkers. From greater productivity to improved retention, applying Whole Brain® Thinking through Herrmann’s complete platform gives you the power to transform your workplace and drive business results.
Is There an Ideal HBDI®?
No. The HBDI® is an assessment — not a test — and preferences are just that, a preference we measure in degree: low, medium, and high. There are no right or wrong answers. There's no such thing as a good, bad, right, or wrong profile. The HBDI® reveals your thinking preferences and what gives you energy, and what does not.
A higher score in a quadrant indicates you’re more likely to prefer tasks requiring that thinking. For example, if you score high in the analytical thinking quadrant, you likely prefer tasks that require logical reasoning and problem-solving.
The HBDI® profile is a tool to help you understand your strengths, challenges, preferences, and areas you might avoid. The HBDI® also helps you understand where your colleagues stand. From there, you can develop strategies and habits to exercise your skills in lower-preference areas.
With the HBDI® as a jumping-off point, Herrmann’s platform applies the Whole Brain® Thinking methodology with many supporting tools to help you create a common language within your organization. Better understand your thinking, create new habits, and widen your lens so you and your team can learn to bring your Whole Brain® to work.